Molarity and dilutions worksheet answer key – Unveiling the intricacies of molarity and dilutions, this worksheet answer key serves as an indispensable resource for students and professionals seeking a comprehensive understanding of these fundamental concepts. Through lucid explanations and step-by-step guidance, this document empowers individuals to navigate the complexities of molarity calculations, dilution formulas, and their diverse applications.
Delving into the realm of molarity, the worksheet answer key meticulously Artikels the concept, exploring its significance in quantifying the concentration of solutions. It provides a structured framework for calculating molarity, complemented by illustrative examples that solidify understanding. Furthermore, the key delves into dilution calculations, presenting a systematic approach to determine the concentration of diluted solutions.
A comprehensive table of dilution calculations serves as a valuable reference, showcasing the practical application of these principles.
Molarity and Dilutions: Molarity And Dilutions Worksheet Answer Key

Molarity and dilutions are essential concepts in chemistry that play a crucial role in various fields. Molarity refers to the concentration of a solution, while dilutions involve altering the concentration of a solution by adding solvent. Understanding these concepts is vital for accurate preparation and handling of solutions in scientific experiments and practical applications.
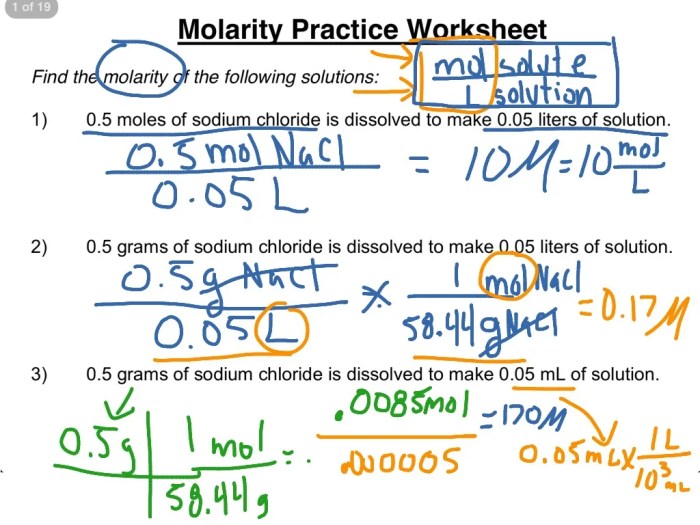
Molarity Calculations
Molarity (M) is a measure of the amount of solute (in moles) dissolved in a specific volume of solution (in liters). It is calculated using the formula:
M = moles of solute / liters of solution
For example, if you have 0.5 moles of sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolved in 2 liters of water, the molarity of the solution would be 0.25 M.
Dilution Calculations
Dilution calculations involve determining the new concentration of a solution after adding solvent. The formula used for dilution calculations is:
M₁V₁ = M₂V₂
Where:
- M₁ is the initial molarity of the solution
- V₁ is the initial volume of the solution
- M₂ is the final molarity of the solution
- V₂ is the final volume of the solution
For example, if you have 100 mL of a 1 M NaCl solution and add 200 mL of water, the new concentration of the solution would be 0.5 M.
Worksheet Answer Key, Molarity and dilutions worksheet answer key
An answer key for a worksheet on molarity and dilutions should provide detailed explanations for each answer. The answer key should be organized in a clear and concise manner, making it easy for students to understand the concepts and apply them to solve problems.
Applications of Molarity and Dilutions
Molarity and dilutions have wide applications in various fields, including:
- Chemistry: Determining the concentration of solutions for reactions and experiments.
- Medicine: Preparing solutions for injections, intravenous fluids, and drug delivery.
- Environmental Science: Measuring the concentration of pollutants in water and soil samples.
- Food Science: Determining the concentration of nutrients and additives in food products.
Safety Considerations
When working with molarity and dilutions, it is essential to follow safety considerations:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves and eye protection.
- Handle chemicals in a well-ventilated area.
- Dispose of chemicals properly according to local regulations.
FAQ
What is the formula for calculating molarity?
Molarity = Moles of solute / Volume of solution in liters
How do you perform dilution calculations?
M1V1 = M2V2 (Initial concentration x Initial volume = Final concentration x Final volume)
What are the applications of molarity and dilutions?
Preparing solutions for chemical reactions, standardizing solutions, and determining the concentration of unknown solutions