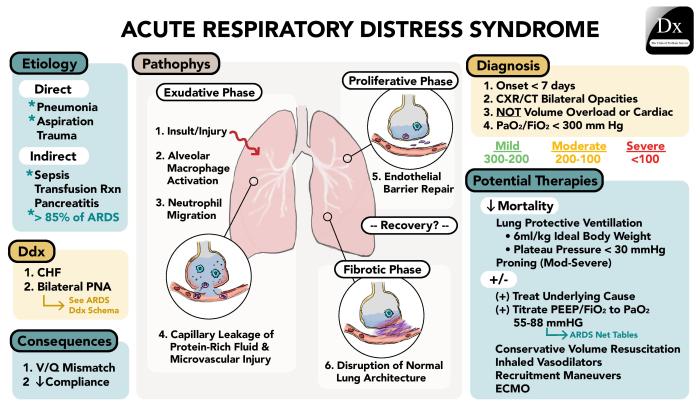
Clinical manifestations and assessment of respiratory disease form the cornerstone of effective diagnosis and management of these prevalent conditions. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the clinical signs and symptoms, assessment techniques, and differential diagnosis of respiratory diseases, offering healthcare professionals a valuable resource for enhancing patient care.
Clinical Manifestations of Respiratory Disease: Clinical Manifestations And Assessment Of Respiratory Disease

Respiratory diseases encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the respiratory system, from the nose and throat to the lungs. These diseases can manifest with a variety of clinical signs and symptoms that provide valuable clues for diagnosis and management.
Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, or dyspnea, is a common symptom of respiratory disease. It can range from mild discomfort to severe distress and can be experienced during exertion or even at rest.
Cough
Cough is a protective reflex that helps clear the respiratory tract of mucus, foreign particles, or irritants. It can be productive, bringing up mucus or phlegm, or non-productive, with no sputum production.
Wheezing
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound that occurs during breathing. It is caused by narrowed airways, which can be due to inflammation, mucus production, or bronchospasm.
Chest Pain
Chest pain is another common symptom of respiratory disease. It can vary in character and location, depending on the underlying cause. Chest pain can be pleuritic, sharp, and aggravated by coughing or deep breathing, or it can be dull and aching.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of extreme tiredness or lack of energy. It is a common symptom of many chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and COPD, and can significantly impact quality of life.
Assessment of Respiratory Disease
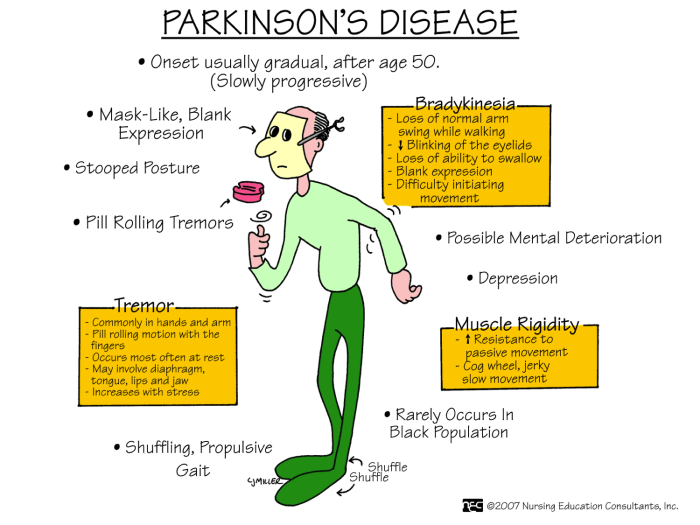
A thorough assessment is essential for accurate diagnosis and management of respiratory diseases. This involves a comprehensive history and physical examination, as well as various diagnostic tests.
Physical Examination
Physical examination includes inspection of the chest and auscultation of the lungs. Inspection can reveal abnormalities in chest shape, respiratory rate, and movement. Auscultation allows the healthcare provider to listen for abnormal breath sounds, such as wheezes, rales, or crackles.
Spirometry, Clinical manifestations and assessment of respiratory disease
Spirometry is a non-invasive test that measures lung function. It involves blowing into a mouthpiece connected to a spirometer, which records airflow and volume. Spirometry can help diagnose and monitor respiratory diseases, such as asthma and COPD.
Chest X-ray
A chest X-ray provides a visual representation of the lungs and surrounding structures. It can detect abnormalities in lung tissue, such as infiltrates, masses, or pleural effusions.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
A CT scan is a more detailed imaging test that provides cross-sectional images of the lungs. It can reveal structural abnormalities, such as bronchiectasis or interstitial fibrosis, and can be used to guide biopsies or other procedures.
Top FAQs
What are the most common clinical manifestations of respiratory disease?
Shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, chest pain, and fatigue are among the most prevalent clinical manifestations.
Why is a thorough assessment crucial in respiratory disease management?
Assessment helps identify the underlying cause, determine disease severity, guide treatment decisions, and monitor disease progression.
What are the key methods used to assess respiratory function?
Physical examination, spirometry, chest X-ray, and computed tomography (CT) scan are commonly employed assessment methods.