Describe the possible echelon forms of a nonzero 22 matrix – Describe the possible echelon forms of a nonzero 2×2 matrix, a topic of paramount importance in linear algebra, unveils the intricacies of matrix transformations and their profound implications in various mathematical applications. This discourse delves into the concept of echelon forms, elucidating their significance and unraveling the systematic process of row operations employed to achieve them.
By exploring the properties of reduced echelon forms and their uniqueness, we gain a deeper understanding of matrix structures and their behavior under linear transformations.
The significance of echelon forms extends beyond theoretical foundations, as they play a pivotal role in solving systems of linear equations, inverting matrices, and calculating determinants. Moreover, their applications in linear programming, eigenvalue and eigenvector analysis, and understanding the structure of vector spaces solidify their importance in diverse fields of mathematics.
Echelon Forms of a Nonzero 2×2 Matrix: Describe The Possible Echelon Forms Of A Nonzero 22 Matrix
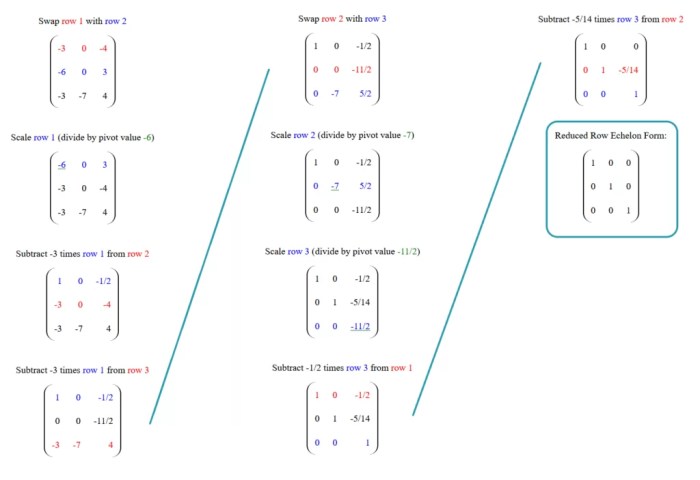
Echelon forms are matrices with a specific structure that simplifies operations and provides insights into the matrix’s properties. Row operations, such as row swapping, multiplying rows by constants, and adding multiples of one row to another, can transform a matrix into echelon form.
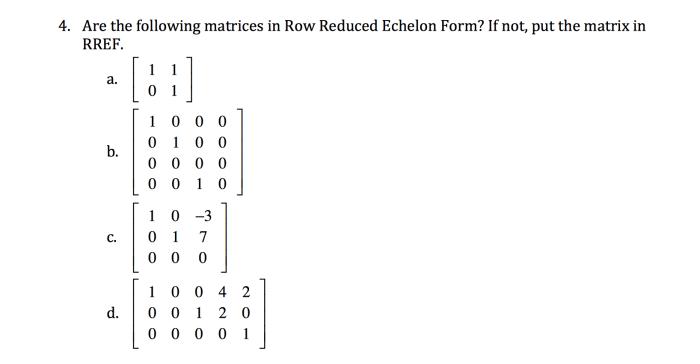
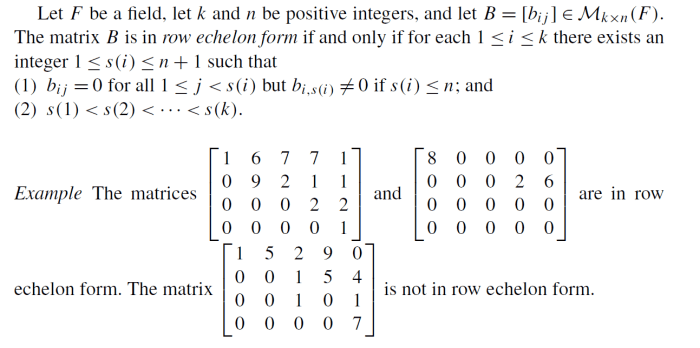
A matrix is in echelon form if it meets the following conditions:
- All rows consisting entirely of zeros are at the bottom of the matrix.
- The first nonzero element in each row (called the leading coefficient) is 1.
- Leading coefficients are to the right of the leading coefficients in the rows above them.
Non-echelon forms are matrices that do not satisfy these conditions.
Reduced Echelon Forms, Describe the possible echelon forms of a nonzero 22 matrix
Reduced echelon forms are a special type of echelon form where every column that contains a leading coefficient has all other elements in the column set to zero. This can be achieved by performing additional row operations on the echelon form.
Reduced echelon forms are unique for a given matrix, and they provide the simplest possible representation of the matrix’s row space.
Echelon Forms in Matrix Operations
Echelon forms play a crucial role in matrix operations, including:
- Solving systems of linear equations: Echelon forms can be used to determine whether a system has solutions and, if so, to find those solutions.
- Matrix inversion: The inverse of a matrix can be found by transforming it into reduced echelon form.
- Determinant calculation: The determinant of a matrix can be calculated using echelon forms.
Applications in Linear Algebra
Echelon forms have numerous applications in linear algebra, including:
- Solving linear programming problems: Echelon forms can be used to find the optimal solution to a linear programming problem.
- Finding eigenvalues and eigenvectors: Echelon forms can be used to find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix.
- Understanding the structure of vector spaces: Echelon forms can be used to determine the basis and dimension of a vector space.
FAQ
What is the significance of echelon forms in linear algebra?
Echelon forms provide a systematic and efficient method for solving systems of linear equations, inverting matrices, and calculating determinants. They simplify matrix operations and reveal the underlying structure of matrices.
How are echelon forms used in solving systems of linear equations?
Echelon forms allow us to determine whether a system of linear equations has a unique solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. They also provide a straightforward method for finding the solution(s) if they exist.
What is the difference between an echelon form and a reduced echelon form?
An echelon form is a matrix that satisfies certain row reduction criteria, while a reduced echelon form is a unique echelon form that has additional properties, such as having leading 1s in each row and 0s below and above each leading 1.