Quiz 2-3 parent functions transformations graphing – Quiz 2-3: Parent Functions, Transformations, and Graphing delves into the fascinating world of mathematical functions, exploring their transformations and the impact they have on their graphs. From linear to exponential functions, we will unravel the secrets of these parent functions and uncover the power of transformations in shaping their behavior.
Throughout this journey, we will delve into the concepts of translation, reflection, and dilation, unlocking the ability to manipulate functions and create new ones with distinct characteristics. Step-by-step instructions and interactive examples will guide you through the process of graphing transformed functions, empowering you to visualize and analyze their behavior.
Parent Functions and Their Transformations
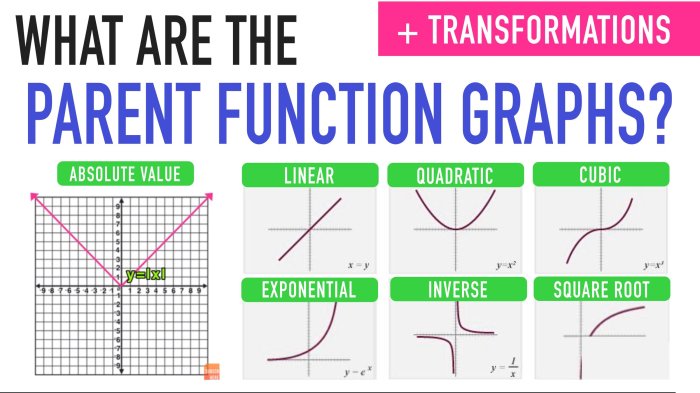
Parent functions are basic functions that serve as the foundation for more complex functions. The most common parent functions are linear, quadratic, absolute value, exponential, and logarithmic functions. Transformations are operations that change the graph of a parent function without changing its basic shape.
The most common transformations are translation, reflection, and dilation.
Translation
Translation moves the graph of a function horizontally or vertically. Translating a function horizontally shifts the graph left or right, while translating it vertically shifts the graph up or down.
Reflection
Reflection flips the graph of a function over the x-axis or y-axis. Reflecting a function over the x-axis changes the sign of the y-coordinates, while reflecting it over the y-axis changes the sign of the x-coordinates.
Dilation
Dilation stretches or shrinks the graph of a function horizontally or vertically. Dilating a function horizontally stretches or shrinks the graph in the x-direction, while dilating it vertically stretches or shrinks the graph in the y-direction.
Graphing Transformed Functions
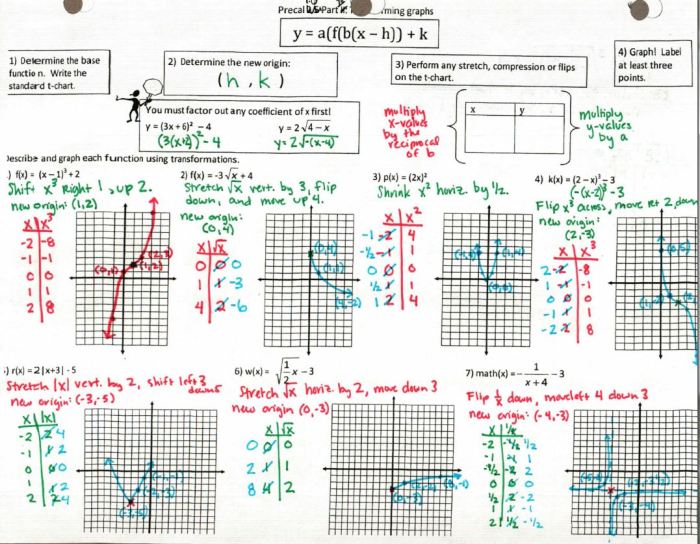
To graph a transformed function, first graph the parent function. Then, apply the transformations in the order they are given. For example, to graph the function f(x) = 2(x – 3) + 1, first graph the parent function f(x) = x.
Then, translate the graph 3 units to the right, and then stretch it vertically by a factor of 2. The final graph will be a parabola that is shifted 3 units to the right and stretched vertically by a factor of 2.
Steps for Graphing Transformed Functions, Quiz 2-3 parent functions transformations graphing
- Graph the parent function.
- Apply the transformations in the order they are given.
- Check your work by graphing the transformed function in a graphing calculator.
Applications of Function Transformations
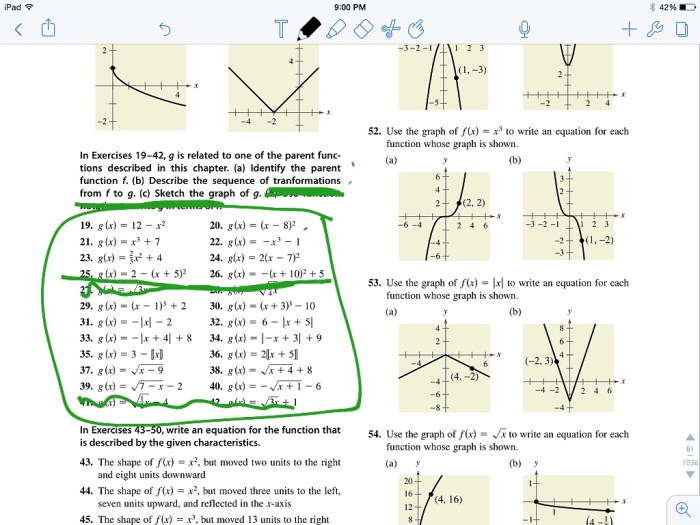
Function transformations are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Modeling real-world phenomena
- Solving equations and inequalities
- Analyzing data
For example, function transformations can be used to model the growth of a population, the trajectory of a projectile, or the spread of a disease.
Examples and Exercises: Quiz 2-3 Parent Functions Transformations Graphing
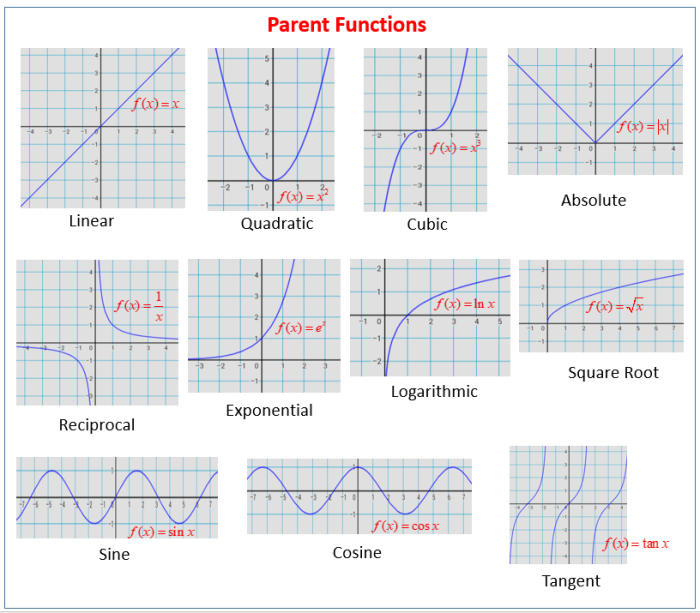
Here are a few examples of graphing transformed functions:
- f(x) = x + 2 (translation 2 units up)
- f(x) = -x (reflection over the x-axis)
- f(x) = 2x (dilation by a factor of 2)
Here are a few practice exercises for graphing transformed functions:
- Graph the function f(x) = 3(x
1) + 2.
- Graph the function f(x) =
2x + 1.
- Graph the function f(x) = 1/2x.
Quick FAQs
What are the different types of parent functions?
The five basic parent functions are linear, quadratic, absolute value, exponential, and logarithmic functions.
How do transformations affect the graph of a parent function?
Transformations can translate, reflect, or dilate the graph of a parent function, resulting in a new function with different characteristics.
What are some real-world applications of function transformations?
Function transformations are used in modeling a wide range of phenomena, such as population growth, projectile motion, and the decay of radioactive substances.